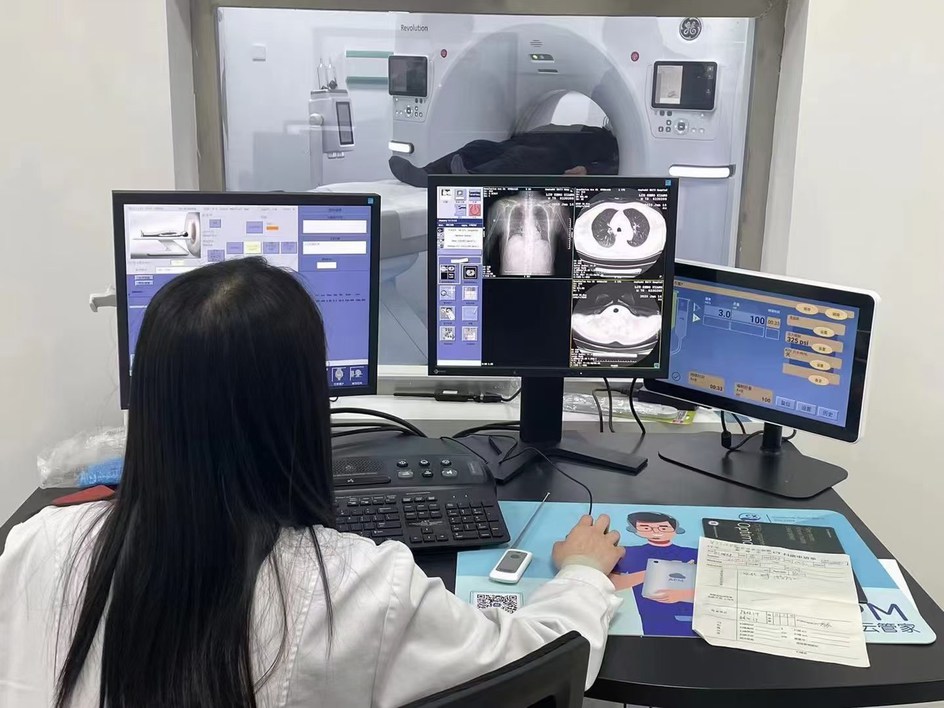
The fusion of artificial intelligence (AI) with cutting-edge imaging technologies is ushering in a new era in healthcare, delivering solutions that are more accurate, efficient, and safe—ultimately improving patient care outcomes.
In today’s rapidly evolving medical landscape, advancements in imaging have revolutionized disease diagnosis, enabling earlier detection and better prognoses. Among these innovations, Photon Counting Computed Tomography (PCCT) stands out as a transformative breakthrough. This next-generation imaging technology significantly surpasses conventional computed tomography (CT) systems in terms of precision, efficiency, and safety. PCCT is set to redefine diagnostic practices and elevate the standard of patient assessments.
Photon Counting Computed Tomography (PCCT)
Traditional CT systems rely on detectors that employ a two-step process to estimate the average energy of X-ray photons (particles of electromagnetic radiation) during imaging. This approach can be likened to blending various shades of yellow into a single, uniform hue—an averaging process that limits detail and specificity.
PCCT, on the other hand, uses advanced detectors capable of counting individual photons directly during an X-ray scan. This allows for precise energy discrimination, akin to preserving all the unique shades of yellow rather than merging them into one. The result is highly detailed, high-resolution images that enable superior tissue characterization and multispectral imaging, offering unprecedented diagnostic accuracy.
Enhanced Imaging Precision
The Coronary Artery Calcium Score, commonly referred to as the calcium score, is a frequently requested diagnostic test used to measure calcium deposits in the coronary arteries. A score exceeding 400 signifies a substantial buildup of plaque, placing the patient at a heightened risk of heart attack or stroke. For a more detailed assessment of coronary artery narrowing, a CT Coronary Angiogram (CTCA) is often employed. This test generates three-dimensional (3D) images of the coronary arteries to aid in diagnosis.
Calcium deposits within the coronary arteries, however, can compromise the accuracy of CTCA. These deposits may lead to “blooming artifacts,” where dense objects, such as calcifications, appear larger than they truly are. This distortion can result in an overestimation of the degree of artery narrowing, potentially affecting clinical decision-making.
One of the standout benefits of Photon Counting Computed Tomography (PCCT) is its ability to deliver superior image resolution compared to traditional CT scanners. This technological advancement mitigates the limitations posed by calcifications, providing clearer and more precise images of the coronary arteries. By reducing the impact of artifacts, PCCT helps minimize unnecessary invasive procedures and enhances diagnostic reliability.
Advancing Diagnostic Accuracy
PCCT also excels in differentiating between various tissues and materials, surpassing the capabilities of conventional CT. A significant challenge in CTCA is imaging coronary arteries that contain metal stents, often crafted from stainless steel or specialized alloys. These stents can create numerous artifacts in traditional CT scans, obscuring crucial details.
Thanks to its higher resolution and advanced artifact-reduction capabilities, PCCT delivers sharper and more detailed images of coronary stents. This improvement allows clinicians to evaluate stents with greater confidence, enhancing the accuracy of diagnoses and improving patient outcomes.
Enhanced Diagnostic Precision
Photon Counting Computed Tomography (PCCT) surpasses conventional CT in its ability to differentiate between various tissues and materials. One major obstacle in CT Coronary Angiography (CTCA) is assessing coronary arteries containing metal stents, typically crafted from stainless steel or alloys. These stents often generate multiple artifacts in standard CT scans, obscuring critical details. PCCT’s superior resolution and advanced artifact-reduction techniques enable it to produce sharper, more detailed images of stents, significantly improving diagnostic accuracy.
Revolutionising Oncology Imaging
PCCT is also transformative in the field of oncology, offering unparalleled accuracy in tumour detection and analysis. It can identify tumours as small as 0.2 mm, capturing malignancies that traditional CT might overlook. Additionally, its multispectral imaging capability—capturing data across different energy levels—provides critical insights into tissue composition. This advanced imaging helps to distinguish between benign and malignant tissues more precisely, leading to more accurate cancer staging and more effective treatment planning.
AI Integration for Optimised Diagnostics
The fusion of PCCT with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning is set to redefine diagnostic imaging workflows. AI-powered algorithms enhance the interpretation of PCCT images, assisting radiologists by identifying patterns and detecting anomalies with greater efficiency. This integration boosts both the accuracy and speed of diagnoses, paving the way for more streamlined and effective patient care.
Enhanced Imaging Precision
The Coronary Artery Calcium Score, commonly referred to as the calcium score, is a frequently requested diagnostic test used to measure calcium deposits in the coronary arteries. A score exceeding 400 signifies a substantial buildup of plaque, placing the patient at a heightened risk of heart attack or stroke. For a more detailed assessment of coronary artery narrowing, a CT Coronary Angiogram (CTCA) is often employed. This test generates three-dimensional (3D) images of the coronary arteries to aid in diagnosis.
Calcium deposits within the coronary arteries, however, can compromise the accuracy of CTCA. These deposits may lead to “blooming artifacts,” where dense objects, such as calcifications, appear larger than they truly are. This distortion can result in an overestimation of the degree of artery narrowing, potentially affecting clinical decision-making.
One of the standout benefits of Photon Counting Computed Tomography (PCCT) is its ability to deliver superior image resolution compared to traditional CT scanners. This technological advancement mitigates the limitations posed by calcifications, providing clearer and more precise images of the coronary arteries. By reducing the impact of artifacts, PCCT helps minimize unnecessary invasive procedures and enhances diagnostic reliability.
Advancing Diagnostic Accuracy
PCCT also excels in differentiating between various tissues and materials, surpassing the capabilities of conventional CT. A significant challenge in CTCA is imaging coronary arteries that contain metal stents, often crafted from stainless steel or specialized alloys. These stents can create numerous artifacts in traditional CT scans, obscuring crucial details.
Thanks to its higher resolution and advanced artifact-reduction capabilities, PCCT delivers sharper and more detailed images of coronary stents. This improvement allows clinicians to evaluate stents with greater confidence, enhancing the accuracy of diagnoses and improving patient outcomes.
Optimised Diagnostics through AI Integration
The combination of Photon Counting Computed Tomography (PCCT) with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning is revolutionising diagnostic imaging processes. AI-driven algorithms play a crucial role in interpreting PCCT scans by efficiently recognising patterns and detecting abnormalities, significantly aiding radiologists. This collaboration enhances both the precision and speed of diagnoses, resulting in more effective and streamlined patient care.
AI-Driven Advancements in Imaging
Medical imaging is entering a transformative phase, powered by AI-enhanced PCCT and advanced high-Tesla MRI systems. For patients with suspected coronary artery blockages or implanted stents, PCCT delivers remarkably accurate scans, reducing reliance on invasive diagnostic methods. Its unparalleled resolution and multispectral imaging capabilities facilitate the early detection of tumours as small as 2 mm, more accurate tissue differentiation, and improved cancer diagnosis.
For individuals at risk of lung disease, such as smokers, PCCT offers an efficient method to identify lung tumours early, all while exposing patients to minimal radiation—comparable to just two chest X-rays. Meanwhile, high-Tesla MRI is proving invaluable in older populations by enabling the early detection of conditions like mild cognitive impairment, osteoarthritis, and other age-related disorders, ultimately enhancing quality of life through timely interventions.
A New Horizon in Medical Imaging
The integration of AI with cutting-edge imaging technologies such as PCCT and high-Tesla MRI marks a significant leap forward in medical diagnostics. These innovations deliver greater accuracy, improved efficiency, and enhanced safety, shaping a future where patient outcomes are better than ever before. This new era of diagnostic excellence is paving the way for more personalised and proactive healthcare solutions.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————-
High-pressure contrast media injectors are also very important auxiliary equipment in the field of medical imaging and are commonly used to help medical staff deliver contrast media to patients. LnkMed is a manufacturer located in Shenzhen that specializes in manufacturing this medical equipment. Since 2018, the company’s technical team has been concentrating on the research and production of high-pressure contrast agent injectors. The team leader is a doctor with more than ten years of R&D experience. These good realizations of CT single injector, CT double head injector, MRI injector and Angiography high pressure injector (DSA injector) produced by LnkMed also verify the professionalism of our technical team – compact and convenient design, sturdy materials, functional Perfect, etc., have been sold to major domestic hospitals and foreign markets.
Post time: Dec-01-2024